What is inflammation?
- Inflammation is the body’s defense system.
- It is the body’s response to any infection or injury, It is characterized by redness, swelling, pain, heat, and a loss of function in the affected area. It occurs when the immune system releases chemicals to protect the body from foreign invaders.
- Its job is to help the body rid of damaged tissues and further the process of healing.
- It does its job by increasing blood flow and supplying white blood cells and other materials needed for healing the infected part of the body.
- Inflammation is a natural process that occurs when the body’s white blood cells and chemicals protect us from infection or injury.
- Infection is caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. These organisms invade and reproduce inside the body and can cause illness or disease. Infection can trigger inflammation as part of the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
What is Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a longer-term type of inflammation that can last for weeks, months, or even years. It is often caused by an underlying condition such as an autoimmune disorder, infection, or allergies. Chronic inflammation can lead to a number of health problems including heart disease, arthritis, and diabetes. To reduce chronic inflammation, it is important to make lifestyle changes such as eating an anti-inflammatory diet and exercising regularly.
What are the common symptoms of chronic inflammation
The common symptoms of chronic inflammation can vary depending on the underlying cause. In general, these can include:
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Chronic fatigue
- Fever and chills
- Weight loss or gain
- Skin rashes or bruising
- Headaches and dizziness
Acute Inflammation
Acute inflammation is a short-term type of inflammation caused by infection, injury, or an allergic reaction. Symptoms usually start quickly and can include redness, swelling, pain, and heat in the affected area. Acute inflammation typically resolves within a few days or weeks with treatment. Treatment may include medications, rest, cold compresses, or hot compresses. acute inflammation
In some cases, medications may also be used to reduce inflammation. Talk to your doctor if you think you may have chronic inflammation.
Inflammation and infection are closely related, but they are not the same. Inflammation is a response to injury or infection, while infection is caused by microorganisms.
What causes inflammation
There are many things that can cause inflammation, including:
- Injury or infection
- Allergies
- Autoimmune disorders
- Certain medications
- Some cancers
Inflammation can also be aggravated by the following
- Eating an inflammatory diet
- Being overweight or obese
- Having a sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking cigarettes
- Exposure to environmental toxins
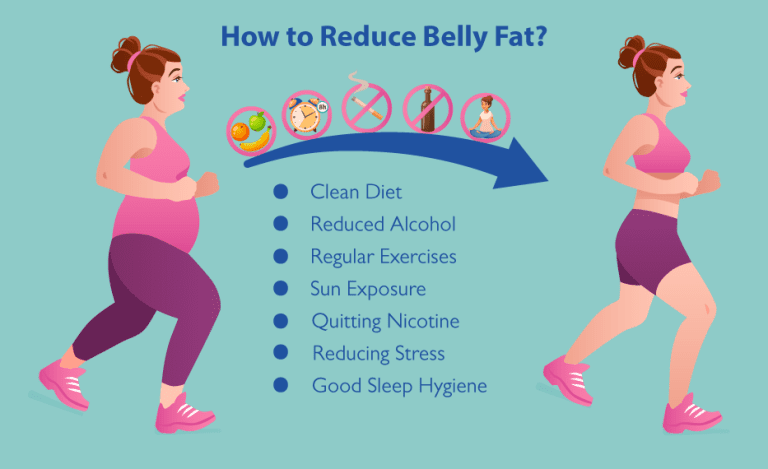
How to reduce inflammation
If you want to reduce inflammation, you need to identify and avoid the things that are causing it. Start by making changes to your diet and lifestyle.
There are many ways to reduce inflammation, both through natural means and medical intervention. Some simple lifestyle changes can go a long way in reducing inflammation, such as:
- Eating a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, ginger, and garlic
- Exercising regularly
- Managing stress levels
- Getting enough sleep
If these measures don’t adequately reduce inflammation, doctors treat inflammation with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, immune suppressants, etc.
Foods that help reduce inflammation
The body’s inflammatory response is a natural mechanism for protecting itself from injury and infection. However, when this response is constantly activated, it can lead to chronic inflammation, which has been linked to a variety of health problems.
There are many lifestyle factors that can contribute to inflammation, but one of the most important is diet. Certain foods can promote inflammation while others can help reduce it.
If you’re looking to reduce inflammation, there are a few key nutrients you should focus on:
Omega-3 fatty acids: These healthy fats are anti-inflammatory and can be found in fish, flaxseeds, and chia seeds.
Turmeric: This spice contains curcumin, a compound with powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
Ginger: Like turmeric, ginger also has anti-inflammatory properties. It can be enjoyed fresh, powdered, or as a tea.
Fruits and vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits and veggies of all kinds are great for reducing inflammation. Several servings of fruit and vegetables spread across the whole day help in better control of inflammation.
Whole grains contain fiber and other nutrients that help reduce inflammation. Choose options like oats, quinoa, and brown rice.
Lifestyle changes to fight inflammation
In addition to dietary changes, there are a few lifestyle modifications that can help reduce inflammation:
Exercise regularly: Exercise has been linked to lower levels of inflammation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise per day.
Reduce stress: Stress is known to trigger inflammation. Take time each day to relax and practice stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
Quit smoking: Smoking is a major contributor to inflammation in the body. If you smoke, talk to your doctor about ways to quit safely.
Get enough sleep: Sleep deprivation has been linked with higher levels of inflammation. Aim for 7–9 hours per night for optimal health and well-being.
Home remedies to fight inflammation
In addition to diet and lifestyle modifications, there are a few simple home remedies that can help reduce inflammation. These include:
- Applying an ice pack or heating pad to the affected area for 10–15 minutes at a time.
- Soaking in a warm bath with Epsom salts.
- Drinking plenty of water and avoiding sugary drinks and alcohol.
FAQ
Yes, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases are both linked to chronic inflammation. High levels of systemic inflammation can lead to a host of health problems, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure.
Ayurveda is an ancient medicinal system that can help reduce inflammation. Ayurvedic treatments include herbs and spices such as turmeric, ginger, and ashwagandha are found to help fight inflammation
Animal products such as beef, pork, and poultry can increase inflammation if not eaten in moderation. Processed meats and foods high in saturated fat can be particularly inflammatory.
Yes, ultra-processed foods are highly processed and typically contain added sugar, fats, and salt. Eating too many of these types of foods can increase inflammation in the body.
Yes, raw foods can help reduce inflammation. Raw vegetables and fruits contain antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation in the body. Eating a diet high in raw foods can also promote health and well-being.
Yes, eating alkaline foods can help reduce inflammation. Alkaline foods are high in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that can help reduce inflammation. Examples of alkaline foods include fruits and vegetables, nuts and seeds, legumes, and whole grains.
Arthritis is a condition characterized by inflammation in the joints. In some cases, inflammation can cause damage to the cartilage, which can lead to pain and stiffness. Reducing inflammation through diet, lifestyle modifications, and medication can help reduce symptoms of arthritis.
Conclusion
Inflammation is a normal part of the body’s healing process, but when it becomes chronic or out of control, it can cause serious health problems. Fortunately, there are many things you can do to reduce inflammation and keep your body healthy. Eating anti-inflammatory foods such as nuts, fruits, and vegetables.
Exercising regularly, managing stress levels and supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids are all effective strategies for reducing inflammation in your body. By following these tips, you can help alleviate symptoms and improve your overall health.